How do you determine the value of an agricultural, forestry or equestrian property?
The value of a property is determined by a combination of various factors such as location, size, condition, features and market demand. In the case of agricultural, forestry, equestrian and related properties, other characteristics naturally play a role, for which a certain level of expertise is required.
Location:
The location of a property plays a decisive role in determining its value. Properties in sought-after locations, e.g. near urban centers, shopping facilities, schools, public transport and business centers, generally have a higher value than properties in less busy and sought-after locations. Of course, this also has an effect on agricultural and historical properties as well as equestrian facilities.
Size:
The size of a property, both in terms of plot size, square footage and the number of usable rooms, is another important factor in determining its value. In general, larger properties are more valuable than smaller ones.
In the case of farm buildings, rounded-off agricultural land (arable land and / or grassland) is a particularly value-enhancing factor, as it improves the usability for livestock farmers.
Condition:
The condition of a property is also important in determining its value. Properties that have been well maintained and modernized are generally more valuable than those that are run down and need a lot of renovation and repair work.
Features:
Certain features or unique selling points of a property, such as high-quality floor coverings, modern technology, exceptional gardens or parks, can also increase its value.
Market demand:
Finally, the current demand for real estate in the area where the property is located also affects its value. If many buyers are looking for properties in a particular area, this can increase the value of the property.
Overall, the value of a property is determined by a combination of these factors as well as other market conditions and trends (interest rate situation, etc.).
In order to be able to market a property, its market value must first be determined as precisely as possible. There are various methods for this, all of which should ideally be used to determine the market value:
Comparative value method:
In this procedure, the comparative value of the property is determined. This is based on the purchase prices of other comparable properties (standard land value) and real estate (standard real estate value) in the region.
Standard land value:
The standard land value is the value for one m² of undeveloped land, assuming that the area is developed. The legal basis for the valuation is the German Building Code (BauGB). The standard land value is calculated from the average of all officially collected values or purchase prices in the relevant category that are typical for the location.
The different categories of standard land values are Standard land value for forestry, agriculture (arable land), agriculture (grassland), land ready for construction in inner and outer areas and commercial building land.
The expert committees for property values are responsible for the assessment. In North Rhine-Westphalia, these are located at the surveying and land registry offices of the independent cities and districts. The standard land values are validated annually.
Asset value method:
In the complex asset value method, the production costs for a property are determined (notional new build) and adjusted according to age. In addition, the land value, which is determined using comparative values or standard land values (see above), is added.
The asset value method is defined by the ImmoWertV in conjunction with the Asset Value Directive and the German Building Code.
A large number of factors are taken into account: Type of building (use, construction method, basement, number of storeys, extension status, roof shape, fittings (...)), age, usable and gross floor area.
For a wide variety of building types - including agricultural buildings such as cattle, pig and poultry barns, multi-purpose halls, etc. - there are standard production costs defined in the Property Value Guideline, divided into various standard levels. Changes in construction costs between the valuation date and the date on which the comparative costs are derived are taken into account through indexation.
The age-related wear and tear or the remaining useful life results from the year of construction and the usual total economic useful life of the respective building, which can also be found in the Property Value Guideline. The determined remaining useful life must be adjusted upwards accordingly, taking into account any renovation measures.
The resulting current value of the property can be corrected due to special property-specific features by means of premiums or discounts (particularly high-quality fittings, maintenance backlog). The general value conditions on the land and real estate market are also taken into account.
In the case of wooded areas, the material value of the growth is determined using a complex procedure (comparison of the stock value and the output value). This requires extensive specialist knowledge.
The value of the land, which is normally determined using the comparative value method described above, is added to the value of buildings or forestry growth determined using the asset value method. This results in the total value of the developed or - in the case of forest land - the "stocked" property.
Income capitalization approach:
The income capitalization approach determines the income value of (investment) properties (rented or leased land and real estate). For this purpose, the net income generated by the properties is capitalized.
The income capitalization approach is defined by the ImmoWertV in conjunction with the valuation guidelines.
Land and buildings are also valued separately in this procedure (comparative value procedure).
The focus is on determining the long-term rent/lease to be generated from the rented/leased space. The amount is influenced by the location, size, facilities, quality and market demand, among other factors.
The income to be generated annually results in the gross annual income. Non-allocable costs such as operating and administration costs, maintenance costs and the risk of loss of rent must be deducted from this. In addition, the return on land value must be deducted in order to determine the net income.
To determine the land value interest rate, the land value is in turn multiplied by the property interest rate, which is also determined by the respective expert committees. The property interest rate depends on the location and use of the property. As with the asset value method, the finite usability of buildings must also be taken into account. The net income is regarded as a constant payment and can therefore be capitalized. The multiplier is derived from the remaining useful life and the property interest rate and can be found in the ImmoWertV table.
After multiplying the net income by the multiplier, the capitalized earnings value of the buildings is obtained. After any additions or deductions, the capitalized earnings value is finally calculated from the value of the buildings and the value of the land.
When determining the market value of properties, the above-mentioned methods are used, if necessary in combination with each other, in order to obtain a value that is as accurate and meaningful as possible. Thanks to our many years of expertise, we can then make a very precise market adjustment so that an appropriate value can be determined as the basis for a market approach.
We are also happy to value your property at a predetermined, manageable price. If subsequent marketing is carried out by our company, the costs for this will be offset or reimbursed. Please contact us without obligation!
More articles & news
February 11, 2026
NEW: Farmstead in a secluded location near Erftstadt
Built in 1973, the farmstead consists of a residential building with separate living quarters for elderly parents and an underground garage, a...
February 10, 2026
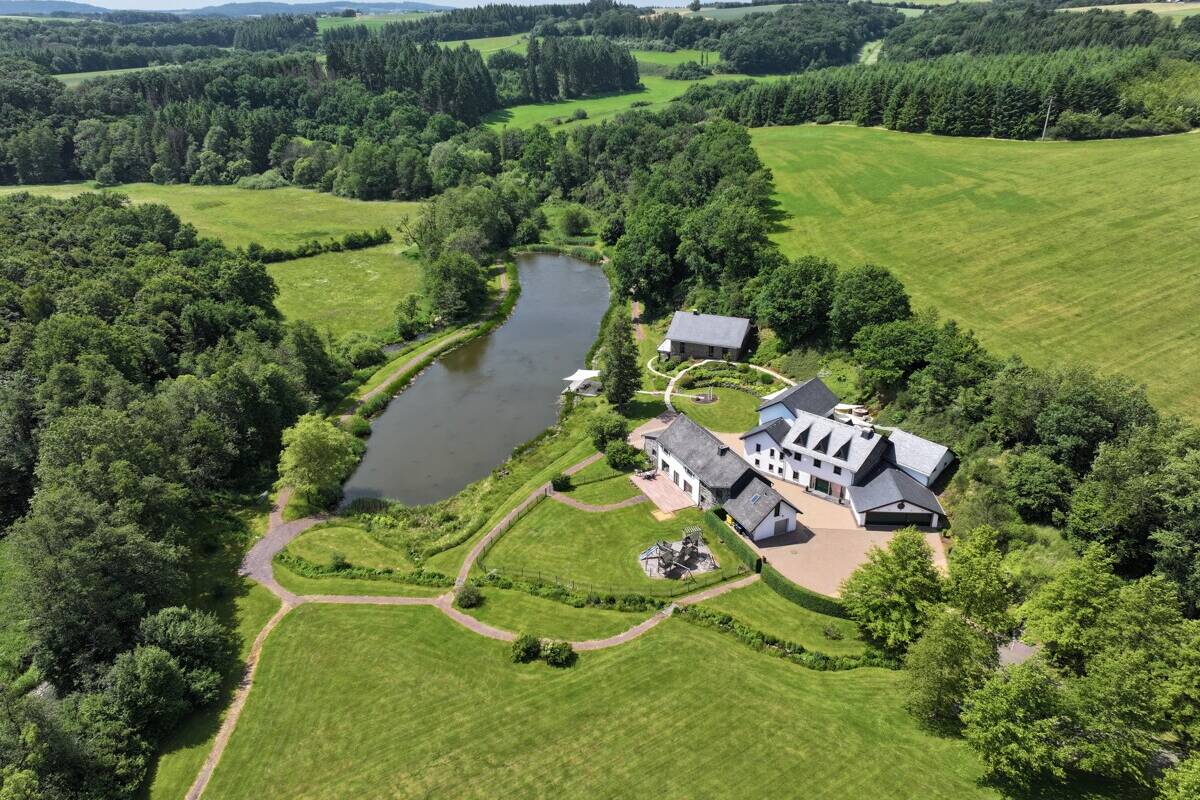
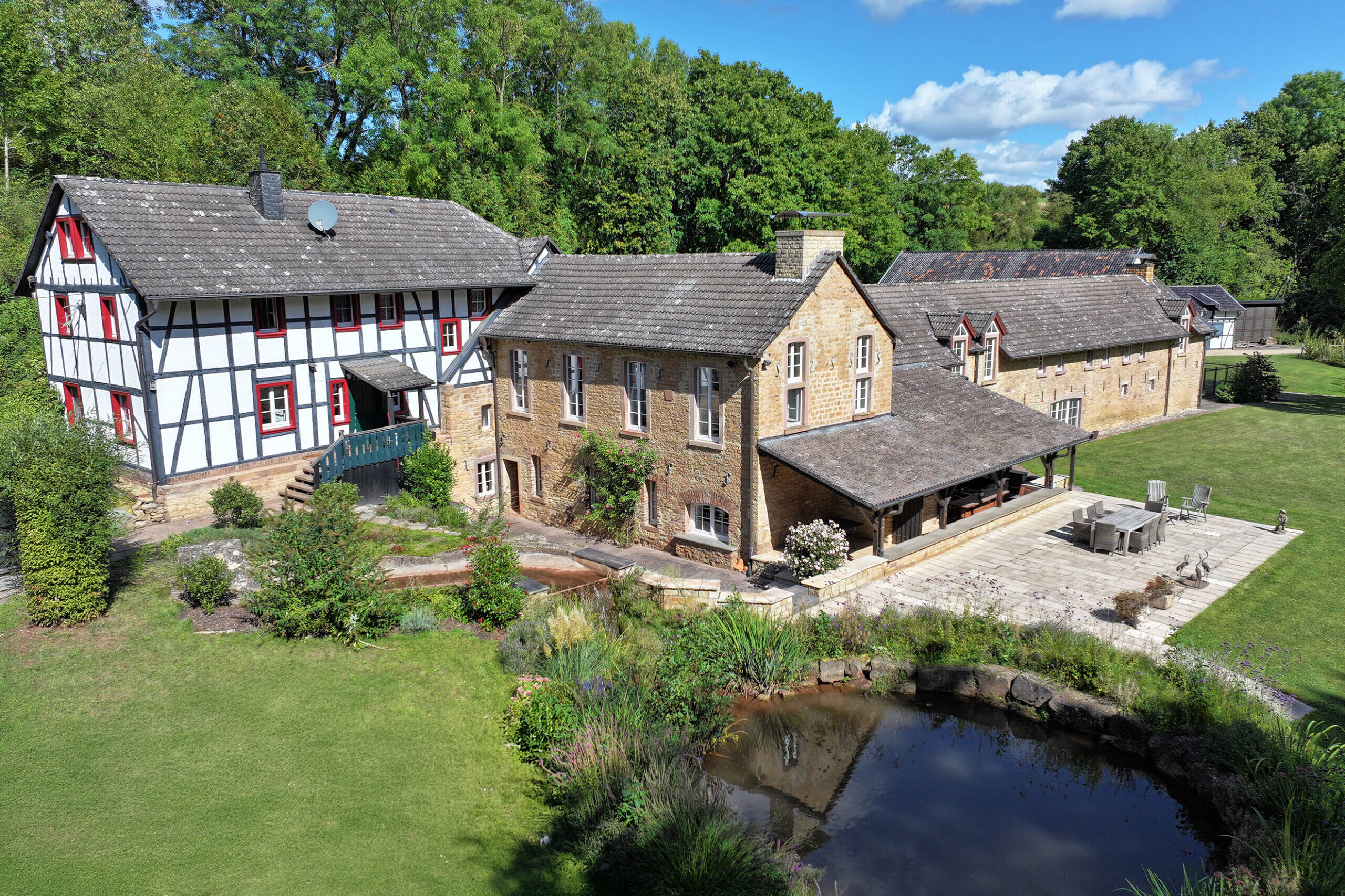
Unique mill property with agricultural and forestry land and hunting opportunities in western Germany
The prestigious property with generous grounds including its own lake as well as largely rounded off agricultural and...
December 23, 2025
Merry Christmas!
We would like to thank all our customers, business partners, and friends for the pleasant cooperation in...
December 16, 2025
14 hectares of consolidated farmland in Erftstadt
The approximately 14 hectares of good-quality farmland is flat and accessible via farm roads.
December 15, 2025
Large areas of farmland with forest cover in the Rhine-Erft district
This special offer comprises two well-developed, consolidated plots (21.6 ha...
December 11, 2025
Historic mill property in the Rhineland successfully brokered!
The future owners are delighted to have a spacious retreat surrounded by beautiful……
December 10, 2025
Two connected farmsteads in the center of Jüchen – Wey
The farm buildings, which have potential for development and are in some cases in need of renovation, each consist of a residential building...
November 26, 2025
The Real Estate Transfer Act (GrdstVG) explained simply
The purchase or sale of farmland, grassland, or forest land differs significantly from traditional...
November 17, 2025
0.8 hectares of arable land and 0.6 hectares of grassland in Linnich
Two areas with good soil quality, easily accessible via farm roads.
November 7, 2025
Farmland, grassland, and forest near Minden
A total of approx. 10 ha of agricultural and forestry land is being sold, which is divided as follows: 1....
November 4, 2025
Land designated for development in Erftstadt-Konradsheim
At present, the area is still predominantly located in an outdoor area under building law. Due to the adjacent...
October 17, 2025
Agricultural privilege - what does that mean?
The so-called agricultural privilege is a central concept in German building planning law....
October 9, 2025
Residual farm with a total of approx. 65 ha of rounded agricultural land in the district of Cuxhaven
The land is mainly arable land. Part of the land is currently undergoing...
September 18, 2025
Small grassland area in Barntrup
It is a small area of grassland with a small wooded area on the outskirts of Barntrup....
September 18, 2025
Farmland and forest in the Lipper Bergland
The land in question is farmland (approx. 2.2 ha) and forest (approx. 1.9 ha).
September 12, 2025
Modern plant cultivation company in Neuss/NRW
This is the site of a plant cultivation company with adjacent arable land. For the...
September 5, 2025
Greif & Meyer at the Forest Farmers' Day 2025
In addition to many exciting technical presentations, numerous good discussions with representatives from the...
August 29, 2025
Exclusive riding facility in the Rhein-Sieg district
With several residential units, riding hall, riding arenas and stables.
August 21, 2025
Magnificent castle estate on the Moselle
The beautiful property offers extensive potential for a variety of use and development concepts.
August 20, 2025
Have you already been in contact with Greif & Meyer, then...
rate us!nnFor each rating, we will finance the planting of a tree in your name in one of the...
August 17, 2025
Greif & Meyer in the LZ: Competent, reputable and discreet
"We are something like a dating agency for farmers - we bring...
August 15, 2025
WANTED: Riding facility or remaining farm
Ideally with adjoining agricultural land. Historic/listed buildings are also welcome.
August 10, 2025
Real estate tracking for owners
As an owner, you have the opportunity to manage all activities relating to your property via our...
July 10, 2025
Rounded-off arable land (19 ha) in the Rhein-Erft district successfully sold!
The land will continue to be used for agricultural production in the long term. We wish the new...
June 29, 2025
Worth knowing - Incidental purchase costs
In addition to the purchase price, there are other costs associated with a real estate purchase such as...
June 26, 2025
The Ravengiersburg monastery has a new owner!
In the foreseeable future, the building is to be converted into a modern senior center with autonomous residential groups. We...
June 13, 2025
Spacious three-sided farm with riding facility in the district of Düren
The riding facility can also be purchased separately as an option
June 8, 2025
Bonn in 10 minutes! Resettlement farm in a secluded location in the Rhein-Sieg district
With a high-quality renovated residential house, retirement section, stables, riding arena and approx. 3 ha of grassland directly on the farm....
June 6, 2025
Agricultural business in the Zülpicher Börde
Arable farm with approx. 36 ha of freehold land in the Zülpicher Börde. The takeover of existing...
May 27, 2025
19 ha arable land in Erftstadt, Rhine-Erft district
This special offer is a completely rounded off, level and easily accessible plot of land.
May 26, 2025
Arable land in Titz
1.6 ha arable land of very good quality in Titz, northern district of Düren, North Rhine-Westphalia.
May 23, 2025
Worth knowing - The land register
The land register is a public register kept at the local court.
May 12, 2025
Well-kept pond in the Westerwald
Consisting of seven individual ponds and a fishing tackle house.
May 8, 2025
Grassland in Kreuzau
1.5 ha grassland area in Kreuzau, Düren district, North Rhine-Westphalia.
May 8, 2025
Rounded-off arable land and grassland in the district of Soest
A total of approx. 8 ha, of which approx. 6.1 ha is arable land and approx. 1.9 ha is grassland.
May 7, 2025
25 ha of top-quality farmland successfully brokered!
The areas located in the Rhine-Erft district and in the area of the city of Cologne have an average...
April 30, 2025
Beautifully situated property in the Düren district
With a variety of possible uses, several residential units and 25.2 hectares of rounded agricultural land, the...
April 30, 2025
Spacious rural property in an absolutely secluded location in the district of Neuwied
with luxurious main house, additional granny apartment, outbuildings and approx. 19.7 ha of adjoining...
April 17, 2025
Farmstead with approx. 10 ha of arable land and grassland in Tecklenburger Land
Formerly used as an agricultural property, partly in need of renovation, in a quiet, outlying and...
April 17, 2025
Square farm in Erkelenz (district)
Versatile property on a total area of approx. 5,400 m². An undeveloped part of the plot of...
April 11, 2025
68 ha of agricultural and forestry land
in the Vulkaneifel district - near the Nürburgring.
April 10, 2025
Arable land and grassland in Goch
A total of approx. 1.3 ha of rounded arable land and grassland in Goch.
April 7, 2025
Magnificent historic square farm with spacious stables, indoor riding arena, riding arena and grassland in the district of Düren
In addition to the lovingly renovated property, there is a small detached house directly adjacent and a...
February 27, 2025
Small arable land in Aldenhoven
0.4 ha with very good creditworthiness (arable number 90)
February 25, 2025
Grassland in Morsbach
A total of approx. 4.9 ha of grassland, divided into three areas. The individual areas amount to approx. 2.7 ha and...
January 14, 2025
Lakeside property with water sports leisure facility in Bavaria
As a future-proof livelihood or interesting investment!
January 7, 2025
Forest estate/own hunt wanted
As the exclusive partner for a foundation from the steel industry, we are looking for a country or forestry estate nationwide,...
January 6, 2025
Cologne in 20 minutes! Spacious courtyard complex with several residential units in Bergisch Gladbach
Very well-kept farmstead of a former agricultural business with extensive......
September 20, 2024
Resettler farm in the district of Aschaffenburg
Consisting of a residential house, several farm buildings and approx. 1.8 ha of rounded arable land and grassland...
September 19, 2024
SUCCESSFULLY SOLD: Idyllically situated country house with adjoining grassland near Aurich, Lower Saxony
We wish the buyer much pleasure with this wonderful property!
September 5, 2024
Fantastically situated property in the Eifel!
The high-quality residential building with swimming pond, sauna house and outbuildings in an elaborately designed park...
July 22, 2024
Forest/own hunt at the gates of Cologne
10 minutes to the city limits. 141 ha in total, including 126 ha of forest and 15 ha of waters/lakes. Black, low,...
July 18, 2024
Arable land in the district of Düren
A total of approx. 2.2 ha.nThe individual plot sizes are approx. 1.4 ha and 0.8 ha.nThe sale of partial plots is...
July 11, 2024
12.6 ha of rounded agricultural and forestry land in the Märkisch district
Divided into approx. 10.4 ha of forest and approx. 2.2 ha of grassland.
May 15, 2024
Grassland and forest areas in Windeck
A total of 12 ha, of which approx. 5.5 ha is grassland and approx. 6.5 ha is forest.
April 5, 2024
SUCCESSFULLY SOLD: Rural property with large pond near Bonn
The purchaser intends a combination of private use and the breeding of rare native species.
March 27, 2024
High-quality riding facility in historic estate in Pulheim/Rhein-Erft district successfully leased!
We wish the new tenants every success with this project!
March 21, 2024
Greif & Meyer in top agrar: Land markets: Are interest rates putting pressure on prices?
PRESSURE IN CONCENTRATION SPACES ...Andreas Eßer assesses the situation in a similar way. He is...
March 4, 2024
Exclusive riding facility in the Rhine-Main area successfully brokered!
The "Nußbaumhof" riding facility changed hands today. A riding school is planned for...
January 22, 2024
15 ha of forest in the North Eifel successfully brokered!
The new owner is a regionally based foundation that uses the forest areas for nature and species conservation....
November 13, 2023
Greif & Meyer in CAPITAL: Forest - the exotic alternative for investors
by Anna Faber. Although it is expensive and time-consuming to maintain, the purchase...
November 9, 2023
Agricultural business in Wermelskirchen successfully brokered!
Yesterday, the farm with a farmstead and a total of 25.2 hectares of agricultural and forestry land...
October 31, 2023
Forstgut Langenohl in Meinerzhagen successfully brokered!
The estate with a total of 157 hectares of rounded agricultural and forestry land and a historic...
October 5, 2023
Specialists for agriculture & forestry!
Greif & Meyer GmbH has been recognized by the German Real Estate Association IVD as a specialist for...
March 31, 2023
Forest estate in Raesfeld successfully brokered!
The new owners intend to cultivate the 184 hectares of land in a natural, careful manner under...
February 20, 2023
Farmland wanted
Investor seeks arable land up to 60 ha in NRW and nationwide. Long-term leaseback is guaranteed.
January 20, 2023
Charmingly situated leisure property with small lake in the Westerwald has found a new owner!
We wish the nature-loving buyer lots of pleasure with this beautiful property!
January 1, 2023
REINFORCEMENT IN THE TEAM!
Since the turn of the year, RT Alois has strengthened our team in the area of hunting and earthworks ;-) We wish him a...
October 6, 2022
Equestrian facility "Asbacher Höhe" successfully brokered!
The equestrian center in the Westerwald changed hands yesterday. We wish the new owners...
October 5, 2022
511 ha forestry operation in the southern Eifel successfully brokered!
Greif & Meyer is brokering a traditional hunting and forestry business with a spacious mill estate and 3...
November 4, 2021
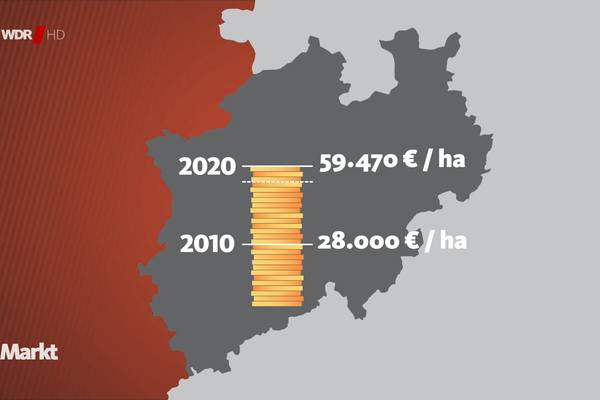
Consumer magazine WDR Markt 3.11.2021: Interview with Greif & Meyer on the agricultural land market
(In the video from minute 25:00 to 33:50)
July 23, 2021
How to call into the forest... Greif & Meyer interviewed in WirtschaftsWoche on the subject of forests as a capital investment
[...] And it gets even more exotic: super-rich families keep a lot of forest. Because...
February 28, 2020
SAFETY FORST - Greif & Meyer interviewed by procontra magazine on forest investments
Investments in forests are considered sustainable, stable in value and high-yielding....
August 23, 2019
No land in sight - Greif & Meyer in an interview with Handelsblatt
While climate change is reducing the value of German forests, prices are rising...
January 31, 2019
Greif & Meyer in an Immowelt interview
Lease or buy a fish pond: Rights, obligations and costs A...